R7 vs. R9 Credit Rating: What’s the Real Difference for Your Future?
If you’ve ever looked at a professional Canadian credit report (the one lenders see, not just the "score" on your banking app), you’ve seen the "R" ratings. These codes are the shorthand lenders use to judge your character. While most people obsess over their 3-digit score, in 2026, savvy borrowers know that the Rating is what actually determines your interest rate for a mortgage or a car loan.
The two most dreaded letters in the alphabet for someone in debt are R7 and R9. In the eyes of Equifax and TransUnion, these codes tell a story of a financial crisis. But they aren't the same. One is a "negotiated peace treaty," while the other is "financial total war." Understanding the difference is the key to deciding whether you should file a Consumer Proposal or a Bankruptcy.
As part of our Debt & Credit Series, this deep dive breaks down the R-rating scale, explains why an R7 is the "Golden Middle Child," and reveals the strategies to rebuild your score to an R1 in record time.
1. The R-Rating Scale: From R1 to R9
In Canada, every credit account (revolving or installment) is assigned a rating from 1 to 9.
- R1 (The Goal): You pay within 30 days of the due date. This is "Perfect Credit."
- R2 – R5: These indicate how many months you are behind (e.g., R3 means you are 60 to 90 days late).
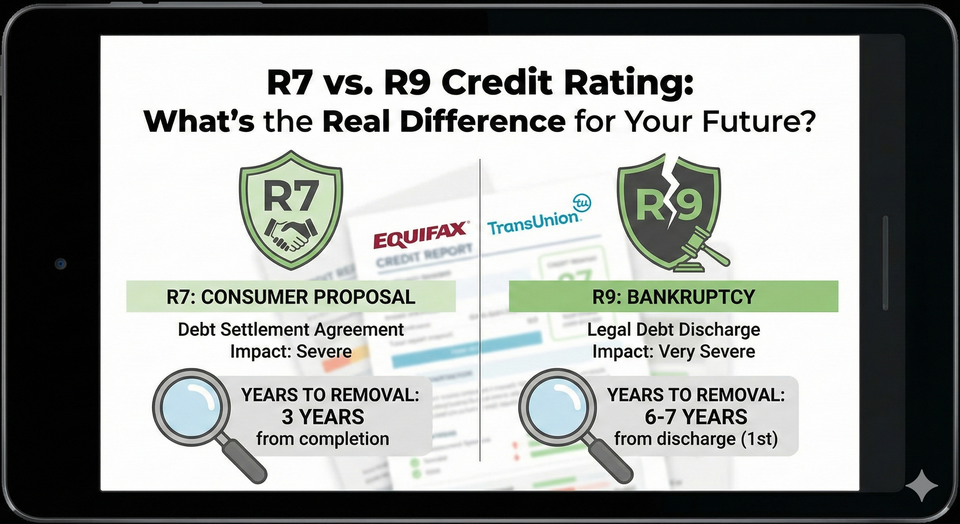
- R7 (The Settlement): You have made a "special arrangement" to settle your debts. This is the code for a Consumer Proposal or a Debt Management Plan.
- R9 (The Default): This is the lowest possible rating. It means the debt is "bad," in collections, you’ve moved without a forwarding address, or you have filed for Bankruptcy.
2. R7 vs. R9: The Timeline Battle
The biggest difference between these two ratings isn't just the "stigma"—it's the Time.
The R7 Timeline (Consumer Proposal)
- How Long? An R7 stays on your report for 3 years after your final payment OR 6 years from the date you filed, whichever comes first.
- The Hack: If you pay off your 5-year proposal in 2 years, the R7 vanishes much faster (5 years total instead of 6).
The R9 Timeline (Bankruptcy)
- How Long? For a first-time bankruptcy, an R9 stays on your report for 6 to 7 years after you are discharged.
- The Reality: Since a standard bankruptcy takes 9 to 21 months to discharge, the R9 can linger for nearly 8 to 9 years from the day you started. If it’s your second bankruptcy, that clock jumps to 14 years.
Credit Rebuild Hacks
This deep dive identifies the specific "Credit Engineering" moves that help you transition back to a prime borrower status.
1. The R9 Collection Trap (Zombie Items)
R9 collection item removal hack.
- The Street Angle: Sometimes, a debt is listed as an R9 (Collections) and an R7 (Proposal). This is "Double Jeopardy."
- The Hack: Once your proposal is finished, all debts included must show a $0 balance.
- The Strategy: If an old credit card is still showing an R9 balance after you have your "Certificate of Full Performance," you must file a Consumer Dispute with Equifax and TransUnion immediately. This one move can jump your score by 50 points overnight.
2. The R7 Mortgage Transition Rule
Many users search for "mortgage with R7 rating Canada 2026."
- The Street Angle: "A-Lenders" (big banks) won't touch you while you have an active R7.
- The Hack: You don't have to wait for the R7 to be removed to get a mortgage.
- The Strategy: Most "B-Lenders" (like Home Trust or Equitable Bank) will give you a mortgage if you have been discharged for 2 years and have re-established credit.
- The Move: Re-established credit means having two new credit products (like a secured card and a car loan) with 24 months of perfect R1 payment history.
3. The Secured Card Jumpstart
A rising search in 2026 is "how to get R1 credit rating after consumer proposal."
- The Hack: Do not wait until the proposal is over to rebuild.
- The Strategy: Open a Secured Credit Card (like Neo Financial or Capital One) the day you file your proposal.
- The Move: By the time you finish your 3 or 5-year proposal, you will already have 60 months of "Perfect R1" history on that new card. This "shadow history" ensures that the day your R7 falls off, your score doesn't just "recover"—it soars.
4. Equifax vs. TransUnion: The Removal Race
Why is the R7 gone from one report but not the other
- The Reality: They use different math.
- Equifax: 3 years after completion or 6 years from filing.
- TransUnion: 3 years after completion or 6 years from the date of default.
- The Hack: If you were 6 months behind before you filed the proposal, TransUnion might actually remove the R7 sooner than Equifax because their clock started earlier. Check both reports for free via Borrowell or Credit Karma.
5. The Purge Date Verification
When will my bankruptcy be removed 2026.
- The Hack: Check the "Purge Date."
- The Strategy: On your official credit report, there is a field called "Estimated date of removal."
- The Move: If your bankruptcy was discharged in 2020, and the removal date says 2027, but you are in Ontario (where it's 6 years), you can call the bureau to have it purged early. Don't let a "Ghost Bankruptcy" haunt your 2026 mortgage application because of a clerical error.
4. Summary: The R7 vs. R9 Comparison Table
| Feature | R7 (Consumer Proposal) | R9 (Bankruptcy) |
| Lender Perception | "They tried to pay us back." | "They walked away." |
| Asset Seizure | None. You keep everything. | Maybe. Depends on equity. |
| Removal Date | 3 yrs post-pay / 6 yrs total. | 6–7 yrs post-discharge. |
| Credit Access | B-Lenders after 2 years. | Sub-prime only for 6+ years. |
| Best For... | Asset protection & steady income. | No assets & no ability to pay. |
R7 vs R9 Credit Rating
What is the difference between R7 and R9 credit ratings in Canada? An R7 rating indicates you have made a special arrangement to settle your debt, typically through a Consumer Proposal; it stays on your report for 3 years after completion. An R9 rating is the lowest possible score, indicating Bankruptcy or a debt in collections; it remains for 6 to 7 years after discharge. R7 is generally viewed more favorably by lenders because it demonstrates an effort to repay a portion of the debt, allowing for faster credit rebuilding and mortgage eligibility.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Can I get an R1 rating while in a consumer proposal?
A: Your old accounts will stay at R7, but any new credit you open (like a secured card) will report as R1 as long as you pay on time. This is how you "dilute" the bad credit with good credit.
Q: Does an R9 ever go away?
A: Yes. It is not permanent. For a first-time bankruptcy, it is automatically purged after 6 to 7 years. You do not need to pay a "Credit Repair" company to have it removed; it is a legal requirement of the credit bureaus.
Q: What if I have an R9 because of a mistake?
A: If a debt is listed as R9 (Collections) but you have already paid it or it's over 6 years old, you can file a dispute to have it removed.
Q: Can I rent an apartment with an R7 or R9?
A: It is more difficult, but not impossible. Large corporate landlords may decline you, but private landlords are often willing to accept you if you show proof of income or offer a larger deposit/co-signer.
About the Author
Jeff Calixte (MC Yow-Z) is a Canadian labour market researcher and digital entrepreneur specializing in government benefit data and cost-of-living support. As the founder of CanadaPaymentDates.ca and BetterPayJobs.ca, Jeff helps newcomers, students, and workers navigate the Canadian social safety net—from tracking CRA payment schedules to finding entry-level work.
Sources
- Equifax Canada: Understanding Your Credit Report Ratings
TransUnion Canada: Credit Report FAQ - R-Ratings Explained
- FCAC: Credit Report and Score Basics
- LIT Canada: The Difference Between R7 and R9 for Future Borrowing
Note
Official 2026 payment dates and benefit amounts are determined by the Canada Revenue Agency (CRA) and provincial governments. While we strive to keep this information current, government policies and schedules are subject to change without notice. All data in this guide is verified against official CRA circulars at the time of publication and should be treated as an estimate. We recommend confirming the status of your personal file directly via CRA My Account or by calling the CRA benefit line at 1-800-387-1193.
